Question
Hard
Solving time: 10 mins
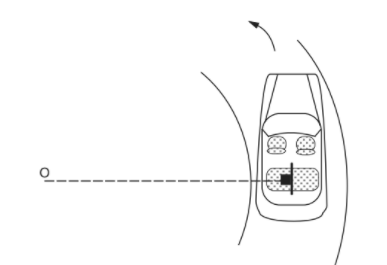
A car moving at a speed of 36 km/hr is taking a turn on a circular road of radius 50 m. A small wooden plate is kept on the seat with its plane perpendicular to the radius of the circular road (In the following figure). A small block of mass 100 g is kept on the seat which rests against the plate. the friction coefficient between the block and the plate is.
(a) Find the normal contact force exerted by the plate on the block.
(b) The plate is slowly turned so that the angle between the normal to the plate and the radius of the road slowly increases.
Find the angle at which the block will just start sliding on the plate.
Found 3 tutors discussing this question
Discuss this question LIVE
15 mins ago
 Text solution
Text solution Verified
Verified
Given :
Speed of the car
Radius of the road
Friction coefficient between the block and the plate
Mass of the small body
(a) Let us find the normal contact force (N) exerted by the plant of the block.
(b) The plate is turned; so, the angle between the normal to the plate and the radius of the rod slowly increases.
Therefore, we have :
On using i and ii, we get:
Speed of the car
Radius of the road
Friction coefficient between the block and the plate
Mass of the small body
(a) Let us find the normal contact force (N) exerted by the plant of the block.
(b) The plate is turned; so, the angle between the normal to the plate and the radius of the rod slowly increases.
Therefore, we have :
On using i and ii, we get:
Was this solution helpful?
13
Share
Report
Filo tutor solutions (7)
Learn from their 1-to-1 discussion with Filo tutors.
1 mins
Uploaded on: 9/28/2022
Was this solution helpful?
64
Share
Report
3 mins
Uploaded on: 6/3/2022
Was this solution helpful?
123
Share
Report

One destination to cover all your homework and assignment needs
Learn Practice Revision Succeed

Instant 1:1 help, 24x7
60, 000+ Expert tutors

Textbook solutions
Big idea maths, McGraw-Hill Education etc

Essay review
Get expert feedback on your essay

Schedule classes
High dosage tutoring from Dedicated 3 experts
Practice questions from Concepts of Physics (HC Verma Part I)
Question 1
Hard
Views: 5,948
Question 4
Easy
Views: 6,241
Practice more questions from System of Particles and Rotational Motion
Question 1
Easy
Views: 5,872
Question 3
Easy
Views: 5,357
Practice questions on similar concepts asked by Filo students
Question 1
Views: 5,572
Question 2
Views: 5,122
Question 3
Views: 5,078
Question 4
Views: 5,657


Stuck on the question or explanation?
Connect with our Physics tutors online and get step by step solution of this question.
231 students are taking LIVE classes
| Question Text | A car moving at a speed of 36 km/hr is taking a turn on a circular road of radius 50 m. A small wooden plate is kept on the seat with its plane perpendicular to the radius of the circular road (In the following figure). A small block of mass 100 g is kept on the seat which rests against the plate. the friction coefficient between the block and the plate is. (a) Find the normal contact force exerted by the plate on the block. (b) The plate is slowly turned so that the angle between the normal to the plate and the radius of the road slowly increases. Find the angle at which the block will just start sliding on the plate. |
| Updated On | Sep 28, 2022 |
| Topic | System of Particles and Rotational Motion |
| Subject | Physics |
| Class | Class 11 |
| Answer Type | Text solution:1 Video solution: 7 |
| Upvotes | 556 |
| Avg. Video Duration | 7 min |



